The technical fixes for obesity are gastric bypass surgery and dietary and behavorial changes. Gastric bypass surgery removes part of the digestive track to make the individual thinner, but teaches them no new eating habits. Thus, the individuals are prone to gaining the weight back. As for changes, it is very easy to slip with the changes, especially in today's high fat, sedentary lifestyle. Thus, there is no truly permanent cure for obesity, only way to hopefull augment people's thoughts and behaviors. As performed today, gastric bypass surgery has two parts:
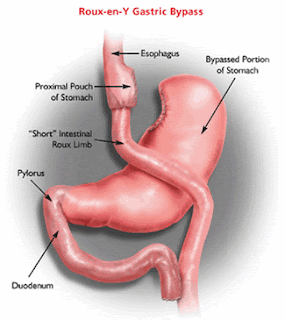
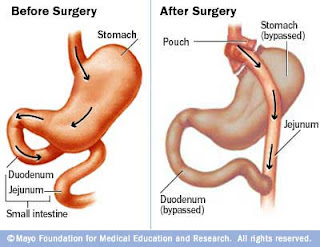
1. Creation of a small stomach pouch
During this part of the surgery, the stomach is divided into a large portion, and a much smaller portion. The small partof the stomach is then sewn or stapled together to make asmall pouch (this part is sometimes called "stomachstapling"). The small stomach pouch can only hold a cup orso of food.With such a small stomach, people feel full quickly and eatless. This strategy is also called "restrictive," since the new stomach size restricts food intake.
2. "Roux-en-Y" creation (bypass)
In this part of the surgery, the new, small stomach pouch isdisconnected from the first part of the small intestine (theduodenum). The surgeon then reconnects the stomach to aportion of intestine slightly further down (the jejunum). This surgical technique is called a "roux-en-Y." After a roux-en-Y, food passes directly from the stomach into the jejunum, bypassing the duodenum. This leads to reduced absorption of calories and nutrients. This weightloss method is called "malabsorptive." Stomach stapling and gastric bypass are typically performed during the same surgery. Together, this surgery is called a"roux-en-Y gastric bypass." The roux-en-Y procedure accountsfor about 80% of all U.S. weight loss surgery procedures.Usually, gastric bypass is performed laparoscopically (usingtools inserted through small incisions in the belly). When laparoscopy is not possible, gastric bypass can be open(laparotomy). This involves a large incision in the middleof the belly.
What to Expect After Gastric Bypass Surgery
Complications
Nearly 10% of people have complications after gastric bypasssurgery. These are usually minor:
Wound infections
Digestive problems
Ulcers Bleeding
Nearly 1% to 5% of people have serious or life-threatening complications:
Blood clot (pulmonary embolism)
Heart attack
Leak in the surgical connections with the intestines
Serious infection or bleeding
The risk of complications is lower at centers that perform more than 100 weight loss surgeries per year. And, when performed by a highly experienced surgeon, deaths in the month following gastric bypass surgery are rare: about 0.2%to 0.5% (less than 1 in 200 people).
Recovery
After gastric bypass surgery, people typically stay in the hospital for two to three days and return to normal activitywithin two to three weeks.
Weight Loss
Weight loss after gastric bypass surgery is often dramatic. On average, patients lose 60% of their extra weight. For example, a 350-pound person who is 200 pounds overweightwould lose about 120 pounds.
Taken from webmd.com(
http://www.webmd.com/diet/weight-loss-surgery/what-is-gastric-bypass-surgery)
by,
rob